Common cylinder knowledge
A cylindrical metal mechanism that guides the piston to reciprocate in a straight line in the cylinder. Air in the engine cylinders by expansion converts thermal energy into mechanical energy; The gas is compressed by the piston in the compressor cylinder to increase the pressure.
The housings of turbines, rotary piston engines, etc., are often referred to as "cylinders". Application fields of pneumatic cylinders: printing (tension control), semiconductors (spot welding machines, chip grinding), automation control, robotics, etc.
①
The basic structure of the cylinder

1. Cylinder barrel
The size of the inner diameter of the cylinder barrel represents the amount of the cylinder output force. The piston should do a smooth reciprocating slide in the cylinder barrel, and the surface roughness of the inner surface of the cylinder barrel should reach Ra0.8um. In addition to the use of high-carbon steel pipes, the cylinder barrel is made of high-strength aluminum alloy and brass.
2. End cap
The end cover is provided with an intake and exhaust port, and some are also provided with a buffer mechanism in the end cover. The rod side end cover is provided with a sealing ring and a dust ring 6 to prevent air leakage from the piston rod and prevent external dust from mixing into the cylinder. The rod side end cover is provided with guide sleeve 5 to improve the guiding accuracy of cylinder.
3. Piston
The piston is the pressurized part of the cylinder. In order to prevent the left and right chambers of the piston from blowing each other, a piston sealing ring 12 is arranged. Also provided with wear ring 11 to improve the guiding of the cylinder.
4. Piston rod
The piston rod is the most important stressed part of the cylinder. High-carbon steel with a hard chrome finish is usually used, or stainless steel is used to prevent corrosion and improve the wear resistance of the seals.
5. Buffer plunger, buffer throttle valve
Piston both sides are provided with buffer plunger 1,3 along the axis direction, there is buffer throttle valve 14 and buffer sleeve 15 on cylinder head simultaneously, when cylinder moves to the end, buffer plunger enters buffer sleeve, cylinder exhaust needs to pass through buffer throttle valve, exhaust resistance increases, produces exhaust back pressure, forms buffer air cushion, plays a buffering effect.
②
Classification of cylinders
As one of the pneumatic components, there are many ways to classify cylinders, mainly introducing two types:
1. Whether the gas pressure from the cylinder piston is one-way or two-way:
1)Single-acting cylinder: The piston of the cylinder can only be pushed by air pressure in one direction, and external force is required when reversing.

2) Double-acting cylinder: The piston of the cylinder is pushed by air pressure in both the forward and reverse directions.
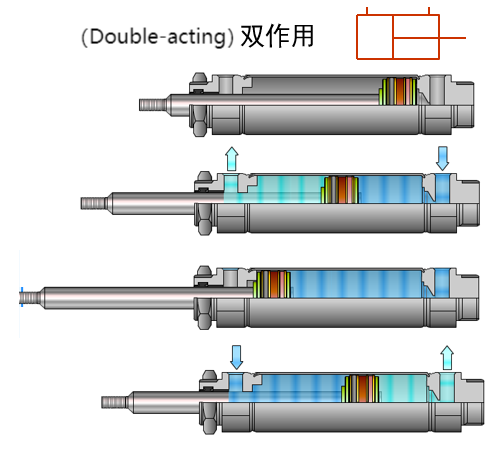
2. According to the function of the cylinder, it can be divided into:
Standard cylinders, compound cylinders, special cylinders, swing cylinders, grippers, etc., among which the more commonly used are free installation cylinders, rodless cylinders, rotary cylinders, double-rod cylinders, thin cylinders, finger cylinders, pen-shaped cylinders, slide cylinders, etc.

(For specific product introduction, please enter the company's website "Product Center")
③
The model of the cylinder
The main representation of the cylinder model is a combination of letters and numbers, the first is a letter to represent the model, the second is a number, which represents the bore, the third number represents the stroke, and the back represents additional functions (according to customer requirements, such as mounting parts and magnetic induction, etc.).
For example, the cylinder model is SCD50×50-20S
The letters and numbers are:
SCD: biaxial double-acting type;
50: Bore 50mm;
The first 100: stroke 50mm;
The second 100: adjustable stroke 20mm;
S: attached magnet;
The following can be used to learn and identify the selection knowledge points against the selection code. (Note: The cylinder catalog will be updated regularly every year, this picture is for reference only, please refer to the latest version for specific parameters)

④
The bore and stroke of the cylinder
Stroke: It is the error distance between the piston rod stretched out and retracted, the cylinder stroke can reach 2000mm, some people will expose the cylinder itself to calculate the stroke, which is wrong.
Bore: is the diameter of the inner wall of the cylinder, the cylinder bore is divided into 32~320mm, the general outer diameter can also be estimated the size of the inner diameter, under the same air pressure, the larger the bore, the greater the output.

⑤
Selection of cylinders
Taking SC as an example, the specific selection procedure is as follows:
1. Selected cylinder series:
According to the purpose of use, bore and stroke range, select the appropriate cylinder series.
2. Select the inner diameter of the cylinder:
According to the load size, running speed and working pressure to determine the cylinder diameter, the important selection steps are as follows: (1) determine the load weight (including the weight of the workpiece, fixture, guide rod and other movable parts); (2) the air pressure selected to be used (the pressure of the compressed air supplying the cylinder); (3) Determine the direction of action of the cylinder.
3. Selected cylinder stroke:
The stroke of the cylinder is related to the use occasion and the stroke ratio of the mechanism. In order to facilitate installation and commissioning, an appropriate margin should be left for the calculated stroke. Use standard strokes whenever possible to ensure fast delivery and reduce costs.
4. Selected installation form:
It is determined by factors such as the installation location and the purpose of use. Generally, a fixed cylinder is used.
5. Select the buffer form:
Depending on the speed of the piston, a buffer device is used. Taking Baidi pneumatic as an example, Baidi pneumatic cylinders are equipped with different buffer devices, customers can choose according to the actual load movement, if the load and speed are large, it is difficult to absorb the impact capacity only by the cushion of the cylinder itself, it is necessary to design a buffer circuit or use an external buffer.
6. Whether the selected cylinder is magnetic:
When the pneumatic system is electrically controlled, a pneumatic cylinder with a magnetic switch can be used.
7. Selected Accessories:
For example, solenoid valves, throttle valves, fittings and even pipes may seem inconsequential but affect performance. Of course, as long as the problem of pneumatic selection is solved, the rest can basically be matched according to the table.
8. Other requirements:
If the working environment is not good, install a dust cap at the protruding end of the piston rod. Oil-free and oil-free lubricated cylinders are available to achieve contamination-free.






